Creation and Manipulation of Video and Audio Footage thanks to AI
Recently a strange video published on YouTube caused a controversy – it was a funny take on Queen Elizabeth’s traditional Christmas message created by Channel 4, a British public-service television broadcaster. They used AI to produce a fake video of the Queen making it look very realistic and if the message itself wasn't obviously a joke, the authenticity of the footage might be kind of hard to assess.
This technology is not so new, as a matter of fact, in the last few years, a number of strange videos showing people swapping faces shown up on the internet.
These videos are nowadays quite easy to create, that’s why there is no shortage of them on YouTube. One of my personal favorites is the one where actor Bill Hader imitates Arnold Schwarzenegger to such extent that his face actually starts to creepily shift in shape until it ends up completely resembling Arnie’s.
Deepfakes – when seeing (or hearing) no longer is believing
These amazing fakes are also dubbed deepfakes (The word “deepfake” comes from the term “deep learning” and of course “fake”) and are a product of the newest in artificial intelligence, or more precisely of its sub-field - machine learning. Machine learning makes it possible to manipulate videos in such way that the entire face of a subject may be replaced with another, while retaining the facial expressions of the original. This is done thanks to an algorithm responsible to replace the face of one subject in a video frame for frame with another subject’s face, while trying to preserve the facial expressions of the original.
Although the most common type of deepfakes are face swaps, the technology behind this opened up so many more possibilities, some still waiting to be discovered. In this article, we list a few interesting examples.
1. Reviving or rejuvenating actors
One recent example of the possibilities machine learning is offering us: a video, whose creator challenged the visual effects department responsible for re-creating Carrie Fisher’s princess Leia character for Rogue One: A Star Wars Story. He used an AI to create a young Carrie Fisher, for which he only needed a dataset – meaning lots of photos of the actress, a computer and one day’s time of computing. Amazing is, that the results he obtained could in all seriousness challenge the actual super-expensive visual effects achieved by a whole team of CGI specialists. This could revolutionize the film industry.
 Source: Image from video by YouTube user Shamook
Source: Image from video by YouTube user Shamook
2. Recreating how historical characters did look like
One interesting recent project produces realistic estimates of how Roman emperors actually looked like. A designer worked with a machine learning app to produce the images based on statues. Thank to this project, photogenic images of historically important people who are long gone come to life. And they are amazing.
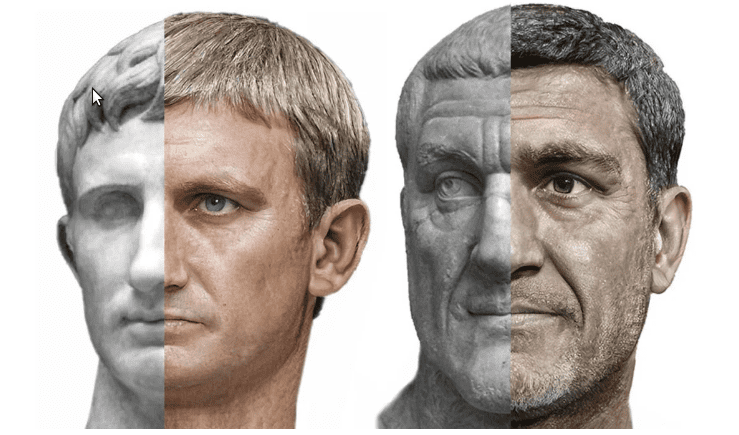 Credit: Daniel Voshart
Credit: Daniel Voshart
3. Enhancing video footage with higher frame rate
Both DAIN (“Depth-Aware Video Frame Interpolation”) as well as the newer and faster RIFE (“Real-Time Intermediate Flow Estimation”) are amazing new techniques which allow us to enhance video tracks so that they have more frames per seconds. They work by using AI to create non-existing frames to fill between existing frames. They are able to interpolate a 30fps video up to 480fps almost without artifacts (visual errors, glitches appearing as a side product of how the AI generates the missing images).
This can be used for example on stop motion animations, giving them a more smooth movement as well as on really old footage, giving a completely new feel to them.

Video by Denis Shiryaev
4. Creating virtual characters
Recently a special Instagram influencer called much attention, which by itself would not be something unusual, but in this case the attention received was thanks to being really special – by not existing in real world. We are talking about Lil Miquela, a hip young girl who likes to party but does not exist. She is generated by an AI, and has almost three million followers. She promotes real life fashion and is able to generate considerable user engagement. With the added advantage that in comparison to real, human influencers, she will never cause an undesired controversy nor has to be paid.
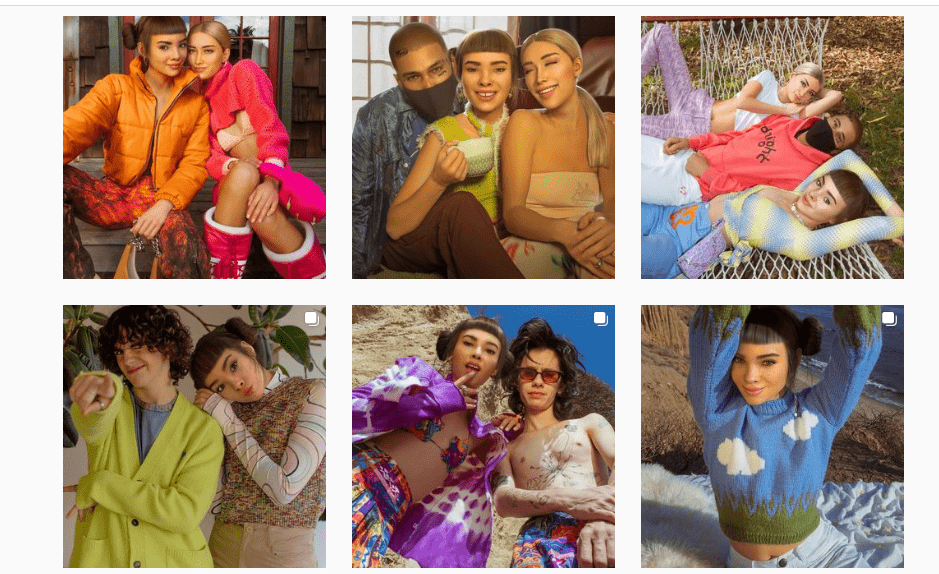 Source: lilmiquela' s Instagram feed
Source: lilmiquela' s Instagram feed
Another example of the practical usage of a digital virtual character – China's Xinhua news agency uses them as news anchors, delivering information on a 24 hours basis. Both the male as well as the female versions look disturbingly genuine and can be mistaken for real people really easily.
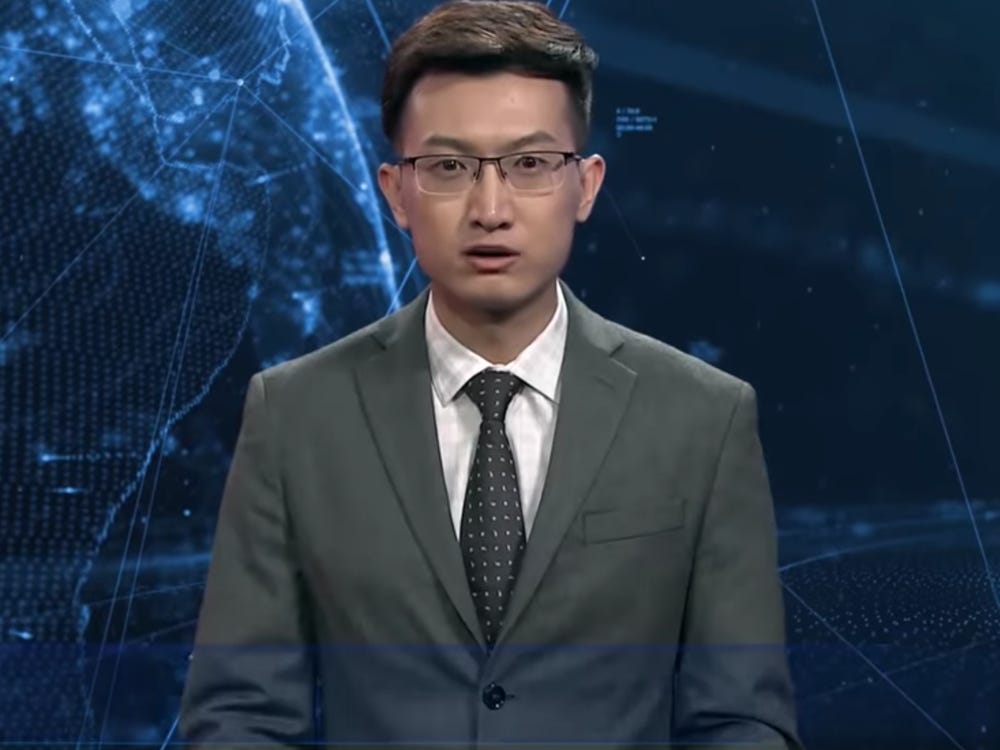 Image source: New China TV/YouTube
Image source: New China TV/YouTube
5. Voice-cloning
Machine learning, apart from the creation of images and videos, can also be applied to sound. Provided with only 5 seconds of recorded voice sample, this neural network-based system for text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis is able to generate speech audio in the voice of many different speakers. Amazing, right? One quick example of practical usage that certainly comes to mind first is voice-acting. Imagine that the actor would only need to deliver 5 seconds of his speech and all the rest would later be generated by an AI. Wow.
6. Creating new music
Researchers at Sony Computer Science Laboratories developed a project called Flow Machines which is able to compose new songs in different musical genres. The Flow Machines system was designed to help music creators by inspiring them and expanding their creativity. It was trained on a large database of songs and generates music by “Exploiting unique combinations of style transfer, optimization and interaction techniques”. We have to admit that the songs it creates are eerily strange and unsettling, but mesmerizing.
Then there is Jukebox: A Generative Model for Music which generates music as well as singing in a variety of genres. It is able to create a music sample if provided with genre, artist, and lyrics as input. The results are fascinating to say the least. For example, the AI created a Katy Perry inspired pop song, with faux lyrics and singing, and it sounds like it came from another dimension, which is uncannily similar to the one we know but somehow distorted.
7. Recreating human faces based on their voice recording
This AI system, called Speech2Face was created by researchers at MIT. It aims at generating the most accurate facial image based on how the subject speaks. It is based on a deep neural network trained on millions of samples, learning to distinguish the correlations between voice and physical attributes of the face. It can guess with a pretty good accuracy the gender, age and race of the person speaking.

Conclusion
The above list is not by any means complete! So many other projects were already made possible thanks to machine learning. They range from quirky and interesting to spectacularly useful, like
- turning drawings into photo and photos into art drawings;
- animating works of art, like the Mona Lisa;
- reconstructing objects into 3D shapes;
- helping self driving cars recognize pedestrians;
And lots and lots more. Which is a great reason to be excited about what the future new uses will bring us. There is most certainly a huge potential in these technologies and we can look forward to how researchers will astonish us next.
Banner image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay

