An easy tutorial on how to import one JS file into another using ES6
Until some years ago, it was not possible to import one js file or block of code from one file into another but since 2015, ES6 has introduced useful ES6 modules. With the module standard, we can use import and export keyword and syntax given to include and export the module in JS respectively.
The static import statement is used to import bindings which are exported by another module. Imported modules are in strict mode whether you declare them as such or not. The import statement cannot be used in embedded scripts unless such script has a type="module".
There is also a function-like dynamic import() , which does not require scripts of type="module".
Backward compatibility can be ensured using attribute nomodule on the script tag.
How we include the js files:
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body> <script type="module" src="script2.js"></script> </body> </html>
script1.js
export default function Hello() {
return "Hello buddy!";
}
script2.js
import { Hello } from './script1.js';
let val = Hello;
console.log(val);
Run the above sample code blocks in your local system/local server, you will get the console output as: Hello buddy!
Code and Syntax Explanation of the code above:
In script1.js, we exported the module with the syntax of : export module
Similarly, in our case, we exported the function Hello by writing the export keyword in the function definition (line number 1 in script1.js). In script2.js, we imported that module by writing the following code/syntax :
import { Hello } from './script1.js';
Right now in script1.js, we have only one module to export but what if we had multiple modules to export? That is also possible with a similar syntax but with a slight modification:
Sample Code for multiple modules:
script1.js
export let Name = (name) => {return "My name is " + name;}
export let Address = (address) => {return "i live in " + address;}
export let Age = (age) => {return "my age is "+ age;}
script2.js
import { Name, Address, Age} from './script1.js';
let val = Name("John");
let age = Age(26);
console.log(val + " and " + age);
In script1.js, we have three modules named Name, Address, and Age. In Script2.js, we imported those modules with similar but little different syntax.
import { Name, Address, Age} from './script1.js';
Note: we didn’t have { } in earlier import code because that was default export ( remember one file can have only one default export).
When we remove that default keyword in previous code of script1.js, we get an error in the console and that error looks like this:
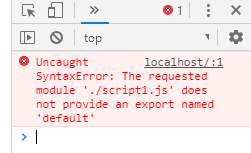
Infact there are two types of exports:
- Named Exports (Zero or more exports per module)
- Default Exports (One per module)
This is only a quick explanation, you can fond more examples at MDN web docs:
Import Statement Reference at MDN
Export Statement Reference at MDN

