Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) enables web clients to make HTTP requests to servers hosted on different origins. CORS is a unique web technology in that it has both a server-side and a client-side component. The server-side component configures which types of cross-origin requests are allowed, while the client-side component controls how cross-origin requests are made.
This article should be your entry point for existing web security standards, most common web attacks and the methods to prevent them. At the end, you will also find out how and why Samy was everyone's hero.(except Rupert Murdoch's, I guess)
CORS
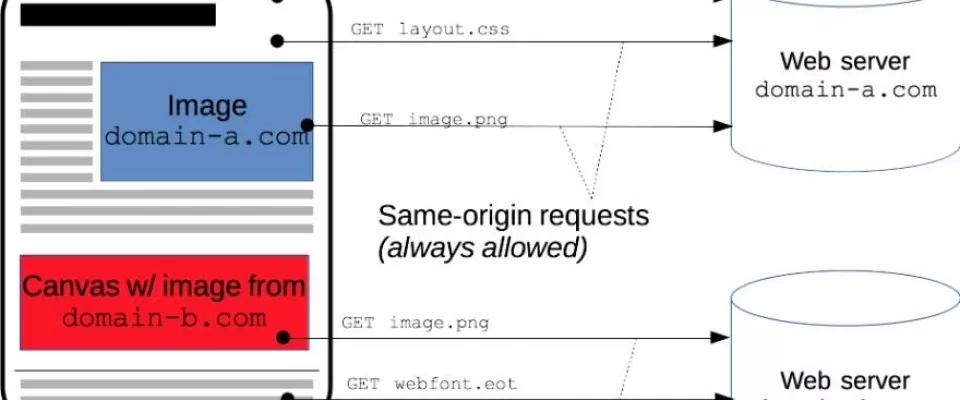
Cross-origin resource sharing, or CORS, is security feature of IE10+, Chrome 4+, Firefox 3.5+ or almost every version of browser released after 2012 except Opera Mini.
When CORS are configured on server that is available on domain
website.com
then resources from that domain those are requested trough AJAX must be initiated from assets that is served from that same domain.
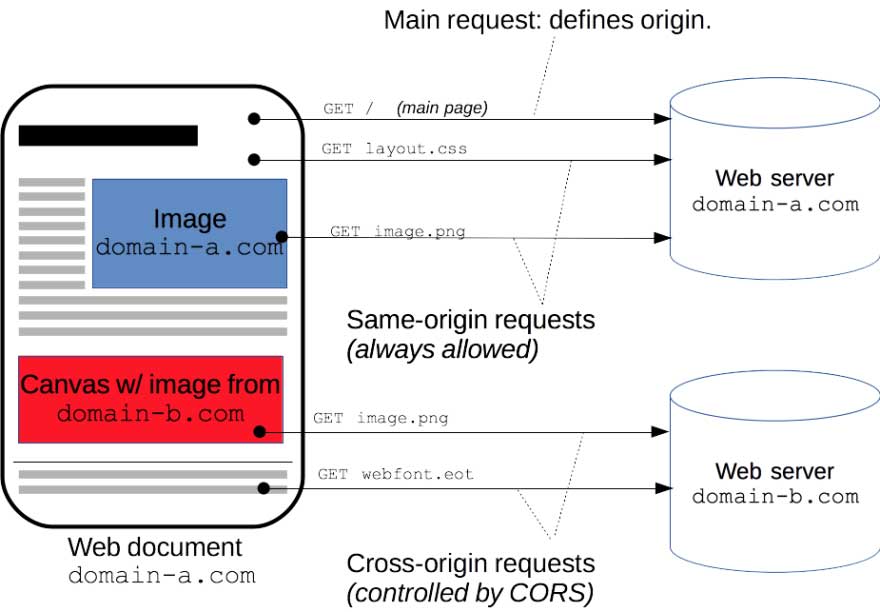
In the other words, if we enable CORS on
domain-b.com
and configure it to allow only
GET
requests from domain
domain-b.com
then if you want to use image available under
https://domain-b.com/images/example.png
in canvas on your website which is hosted on
domain-a.com
, than that image will not be loaded for most of your visitors.
Your resources protected by CORS will still be available when requested by any tool or browser that doesn't respect
CORS policy
.
CORS configuration
CORS are disabled by default which means that there is no adequate server handler that will configure CORS which means that you cannot access resources from different origin in your XHR. Basically, if you don't do anything or specifically enable CORS only for specific domains, then any AJAX request trying to access your resources will be rejected because web browsers are respectful to the
CORS policy
.
This is the reason why you encounter CORS issue when you start developing SPA using VueJS and NodeJS. Your VueJS application is hosted on
http://localhost:8080
and when you try to access NodeJS server application on
http://localhost:8000
you get "
No Access-Control-Allow-Origin header is present
" because those are two different
ORIGINS
(combination of
PROTOCOL
,
HOST
and
PORT
).
Cool fix for CORS issue in VueJS development mode is to set devServer proxy in your
vue.config.js
file as follows:
module.exports = {
...
devServer: {
proxy: 'http://localhost:8000',
},
...
}
To setup CORS in production you should add appropriate listener for
OPTIONS
request. That listener should send response
200
with
no body
but with
Headers
that will define your wanted CORS policy:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://domain-b.com Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET
For more info on how to configure CORS check https://enable-cors.org/index.html, and to dive deeper in
CORS policy
check this book online
XSS
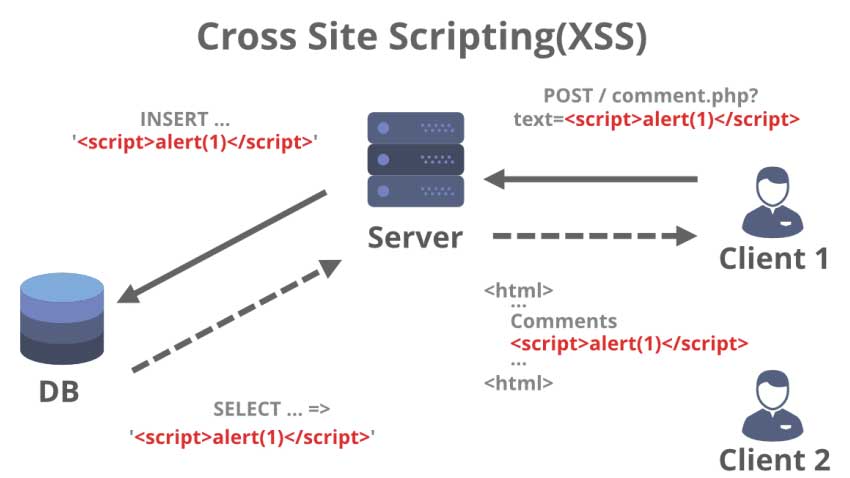
XSS stands for Cross Site Scripting and it is injection type of attack. It is listed as 7th out of top 10 vulnerabilities identified by OWASP in 2017. Cross site scripting is the method where the attacker injects malicious script into trusted website. Vulnerability for XSS is coming from unprotected and not sanitized user inputs those are directly stored in database and displayed to other users.
Attack
Here is an example of attack. The attacker comes on your website and finds unprotected input field such as comment field or user name field and enters malicious script instead of expected value. After that, whenever that value should be displayed to other users it will execute malicious code. Malicious script can try to access your account on other websites, can be the involved in DDoS attack or similar. Visual representation(source geeksforgeeks.org):
Protection
Every value that can be entered by user should be treated as untrusted data and therefore should be processed before storing in database. There most common approaches on processing untrusted data are listed below and ideal method depends on the actual type of the field that you need to process.
1. String validation
Validation is the method where user defines set of rules, and demand untrusted data to satisfy those rules before moving on. This method is good for number values, username, email, password and similar fields with concrete set of syntax rules.
Check for existing libraries for your framework before considering to write validators by your own.
2. String escape
Escape method is useful for cases where you should enable user to use punctuation marks. This method goes through string and looks for special characters, such as
<
>
and replace them with appropriate HTML character entity name. Here is basic function that you could use:
function escapeText(text) {
return text.replace(/&/g, '&')
.replace(/</g, '<')
.replace(/>/g, '>')
.replace(/"/g, '"')
}
Again, check for existing libraries before writing your own.
3. String sanitization
Sanitizing string is used when user is allowed to enter some HTML tags in their comments, articles or similar. The sanitize method goes through text and looks for HTML tags that you specify and removes them. One of most popular libraries that uses this approach is Google Closure.
This method is resource expensive and considered as harmful, so do more research before choosing it.
Best practices
Do string escape on front end, as well! As showed in documentation VueJS by itself escapes string before getting value from variable. Newer versions of Angular also escape strings implicitly, so if you are using Vanilla JS, JQuery or similar you should implement string escape manually.
For more detailed info about XSS and how to properly protect your application if you rotate a lot of untrusted data, please check OWASP cheatsheet on XSS.
CSRF
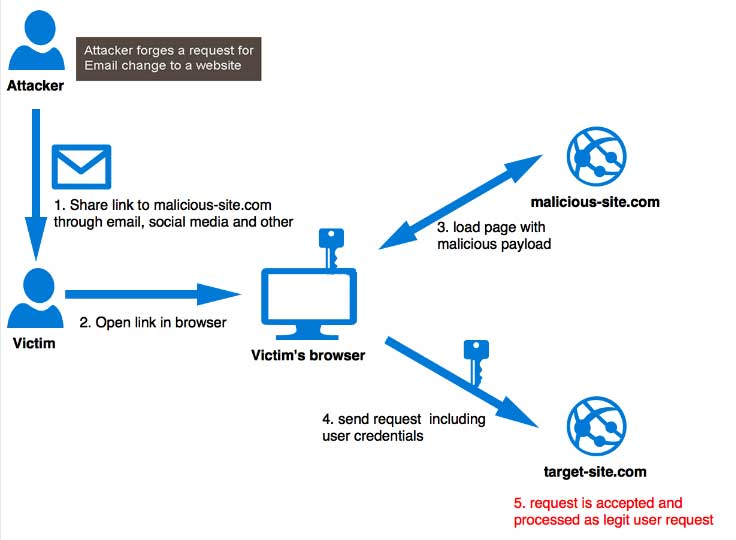
Cross site request forgery or CSRF is a type of attack that occurs when a malicious web site, email, blog, instant message, or program causes a user's web browser to perform an unwanted action on an other trusted site where the user is authenticated. This vulnerability is possible when browser automatically sends authorization resource, such as session cookie, IP address or similar with each request.
ATTACK
Let's suppose that user is logged in to your unprotected stock exchange web application and that you are using either session cookie either JWT cookie for authentication. Attacker also uses your service and is able to check how your API works. Attacker tricks user to execute script(by clicking on SPAM link in email or similar) that will send request to your API
https://www.stockexchange.com/users/withdraw?how_much=all&address=MY_ADDRESS
(terrible API design, don't ask). Since request is executed from browser that sends authentication payload with every request, your stockexchange web server will authenticate user successfully and execute transaction and tricked user will lose all his balance without even being aware of it because everything happened in the background. Visual representation(source miro.medium.com)
PROTECTION
Luckily there are easy to implement patterns that prevent this web attacks. One of the most common pattern is usage of
CSRF token
. Basicly procedure is following:
- Generate unique token for each user's request, so called
CSRF token. - Store it safely on server and send it back to user as payload of response.
- Store
CSRF tokenon client side. - When user tries to execute any state-changing* request send that
CSRF tokenwith request as a payload. - Before executing that request on server side check if
CSRF tokenis present and it is valid.
This is the easiest way to prevent CSRF attack.
Since server's responses are processable in XHR response, that there is no protection on CSRF attack if your web application is XSS vulnerable!
To deep dive check OWASP cheatsheet on CSRF.