If you want to know why React is so successful as a JavaScript library, we need to talk about its main features to find out what it is currently used for and why it is so effective.
When we access an application within a web page that requires continuous requests, if the entire page had to be rendered from zero to one hundred with each of the requests, it would cause slow loads and a disproportionate amount of resources consumed.
This makes React make more sense, since it is a JavaScript library designed to update the information represented on the screen without having to reload the entire process.
Since its release about five years ago, this open source JavaScript library has been a big push for applications such as Instagram, Airbnb or Netflix, which use them within their technology to offer us the best information consuming fewer resources than possible.
The biggest reason React has to perform so well, is that it implements Virtual DOM and instead of rendering it completely with each of the requests, changes are made to a copy in memory and then the algorithm is used to compare the properties of that copy with those of the active version, applying only changes to the parts that are changing such as the weather forecast in a city.
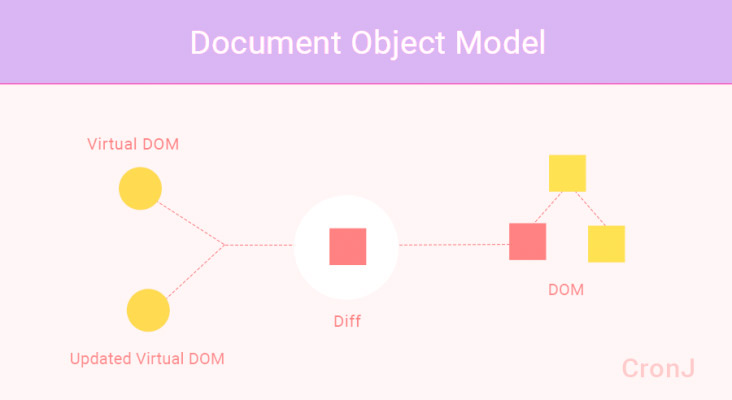
This way, if we have a list where a maximum of 1000 changes can happen, but only five of them change, thanks to React only those five changes are updated without touching the rest, which makes the consumption of resources are lower than the traditional method. In this way React promotes the flow of data in one direction only the place of the bidirectional flow of the traditional frameworks.
Regarding its component architecture, we are talking about independent and reusable entities that encapsulate code to generate different pieces that are capable of developing a specific action. Each component can interact with another as a child component, and this in turn with others, thus generating complex programs in the form of trees.
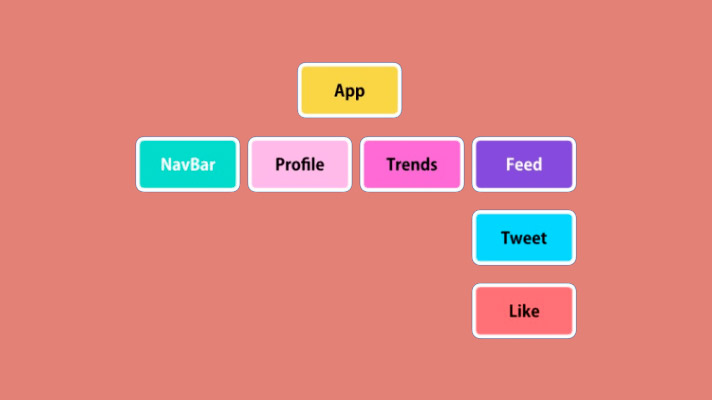
The good thing is that these components can be easily replaced, disabled and edited, and if there is an error it will only be limited to them and will not affect the whole.
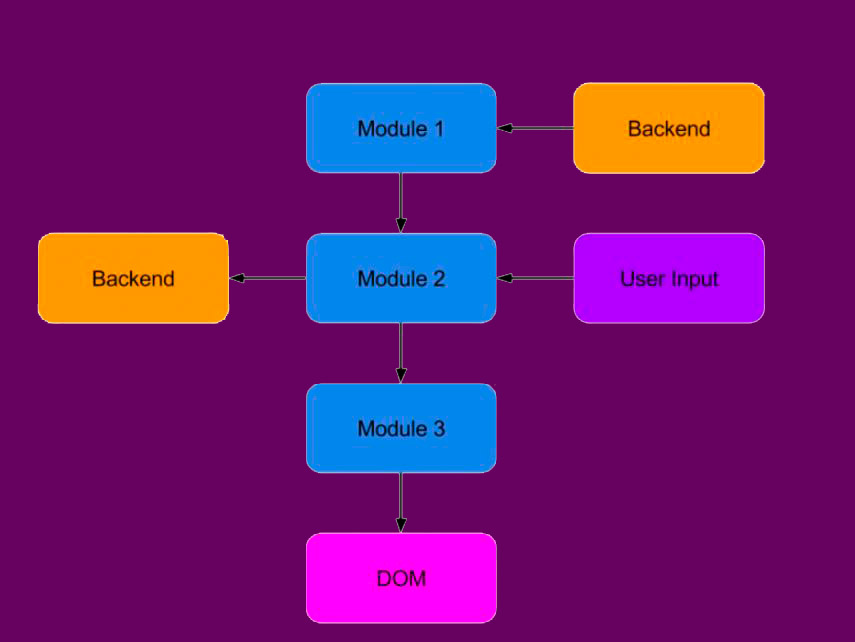
React therefore functions as a unidirectional data flow where each component passes the information to its child components, but not the other way around. This makes it easy to track information and detect errors in all types of applications.

