We've been wanting to write an article about sorting algorithms for some time now because sometimes we forget how useful they can be when we want to optimize our code.
So yesterday we played with the quicksort algorithm in Javascript (one of the most efficient when you have to order arrays). In this article we will tell you all the process we have followed.
We hope it will be useful.
Quicksort performance
Worst-case performance: O(n^2)
Best-case performance: O(n log n)
Average performance: O(n log n)
Not bad considering that the bubble sort has an average O(n^2)
How does Quicksort work?
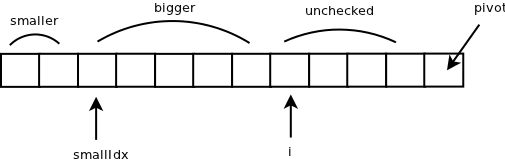
Quicksort works by choosing an element from the array that we'll call a pivot so we can divide the initial array in two:
- the major ones with respect to it
- the minors with respect to it
placing this pivot element in the middle after the separation.
Now for each of these two arrays we will choose a pivot again and repeat the same procedure. There will come a time when the resulting arrays will have either one element or none if there is no longer an element to compare them with. The rest of the elements will have been separated as pivots in some point of the algorithm and they will already be in their correct position.
How do we implement Quicksort?
To implement the quicksort algorithm in javascript we will rely on the pseudocode taken from wikipedia:
algorithm quicksort(A, lo, hi) is if lo < hi then p := partition(A, lo, hi) quicksort(A, lo, p - 1) quicksort(A, p + 1, hi) algorithm partition(A, lo, hi) is pivot := A[hi] i := lo for j := lo to hi - 1 do if A[j] < pivot then swap A[i] with A[j] i := i + 1 swap A[i] with A[hi] return i
The first thing we'll do is define the function that executes the algorithm. Since we want to be able to sort all types of arrays (not only numbers, but also objects) we will allow the function to receive by arguments an additional function that specifies the method of sorting objects:
const defaultSortingAlgorithm = (a, b) => {
if (a < b) {
return -1;
}
if (a > b) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
};
const quickSort = (
unsortedArray,
sortingAlgorithm = defaultSortingAlgorithm
) => {
// quicksort implementation
};
If we look at the pseudocode of the wikipedia, we see that as initial pivot is choosing the end of the array (this can cause performance problems increasing it to O(n^2) when the array is already ordered) so not to complicate too much the article we will focus on him. Also, notice that the pseudocode is written in recursive form since we do not know how many partitions we will have to do as we order the array. With all this we come to:
const defaultSortingAlgorithm = (a, b) => {
if (a < b) {
return -1;
}
if (a > b) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
};
const quickSort = (
unsortedArray,
sortingAlgorithm = defaultSortingAlgorithm
) => {
// immutable version
const sortedArray = [...unsortedArray];
const swapArrayElements = (arrayToSwap, i, j) => {
const a = arrayToSwap[i];
arrayToSwap[i] = arrayToSwap[j];
arrayToSwap[j] = a;
};
const partition = (arrayToDivide, start, end) => {
const pivot = arrayToDivide[end];
let splitIndex = start;
for (let j = start; j <= end - 1; j++) {
const sortValue = sortingAlgorithm(arrayToDivide[j], pivot);
if (sortValue === -1) {
swapArrayElements(arrayToDivide, splitIndex, j);
splitIndex++;
}
}
swapArrayElements(arrayToDivide, splitIndex, end);
return splitIndex;
};
// Recursively sort sub-arrays.
const recursiveSort = (arraytoSort, start, end) => {
// stop condition
if (start < end) {
const pivotPosition = partition(arraytoSort, start, end);
recursiveSort(arraytoSort, start, pivotPosition - 1);
recursiveSort(arraytoSort, pivotPosition + 1, end);
}
};
// Sort the entire array.
recursiveSort(sortedArray, 0, unsortedArray.length - 1);
return sortedArray;
};
As you can see, the first thing we do is clone the array so that the function is immutable and we don't modify the input array. From there we define 3 methods:
swapArrayElements: para intercambiar los elementos de un array
partition: que se encarga de elegir el pivote e intercambiar los elementos para que los más grandes estén a su derecha y los más pequeños a su izquierda. Como se puede ver, hacemos la comparación con el método de clasificación que hemos aprobado o con el que hemos establecido por defecto. Este método devuelve la posición en la que se dejó el pivot.
recursiveSort : implementa el algoritmo quicksort definido en wikipedia. Se debe tener en cuenta que es necesario configurar la condición de parada inicio < fin para que de esta forma se interrumpa la recursión si se han alcanzado arrays de 0 ó 1 elementos.
Finally, the quickSort method invokes recursiveSort by passing it the array as well as the initial and final position.
With this we would already have the quicksort algorithm working in javascript:
const testA = [9, -3, 5, 2, 6, 8, -6, 1, 3];
const testASorted = quickSort(testA);
console.log(testASorted);
const testB = [-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3];
const testBSorted = quickSort(testB);
console.log(testBSorted);
const testC = [3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3];
const testCSorted = quickSort(testC);
console.log(testCSorted);
const testD = [
{
id: 9,
name: "Task 9"
},
{
id: -1,
name: "Task -1"
},
{
id: 5,
name: "Task 5"
},
{
id: 3,
name: "Task 3"
},
{
id: -10,
name: "Task -10"
}
];
const testDSorted = quickSort(testD, (a, b) => {
if (a.id < b.id) {
return -1;
}
if (a.id > b.id) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
console.log(testDSorted);

